AC, DC, plugs and connectors… Which charger should you choose for your electric vehicle?
Charging an electric vehicle means using electric chargers. But how can you know which charger is the best for your electric vehicle? It’s easy to get lost between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) or even between the different types of plugs and connectors available on the market.
Anyway, charging an electric vehicle is not much more complicated than filling up a petrol or diesel. Once you have understood the mechanism around charging, and have considered the characteristics of your vehicle, charging your electric car will be easy.
Current types and their uses
What is the difference between Alternating Current and Direct Current?
There are two types of currents :
- The Alternating Current (AC) is the one produced in a power plant. It circulates in the electrical network and is used to supply homes, buildings, factories, etc.
- The Alternating Current has to be converted into Direct Current (DC) before being stored in the battery of your smartphone or electric vehicle, etc.
Before powering up the vehicle’s battery, the conversion into Direct Current can be done thanks to an on-board charger integrated in the vehicle. The on-board charger is expensive and bulky, that’s why it can limit the charging power.
Direct Current allows the vehicle’s battery to be powered directly, since the conversion from AC current to DC current is carried out by the charge point. This method allows to reach higher charging powers because the cost and the volume of the charger are in the charger and not in the vehicle.
To learn more...
An electric current is a migration of negative charges carried by electrons within the conductive components of an electric circuit. However, electrons do not move around the same way to create alternating current or direct current.
To create Direct Current
Direct Current is an electric current in which electrons flow continuously in one and only direction, from the positive charger to the negative one of the power source.
To create Alternating Current
Electrons delivered by the charger change directions regularly and in high frequencies. They move back and forth regularly.
Which type of power for AC and DC chargers ?
As you can imagine, AC chargers and DC chargers do not deliver the same level of power. If you choose to charge your vehicle by using an AC charger, you will find chargers delivering powers from 3,5 kW to 22 kW. However, if you choose to charge your vehicle on a DC charger, you will find chargers delivering powers from 24 kW to 350kW.
If you want to learn more about the different level of powers, here is an article that might interest you kW, kVA, kWh... Better understand the electric mobility environment
AC or DC chargers : which one to use ?
- AC chargers are the most suitable and least expensive when the vehicle is parked for a long period of time. It allows you to charge your vehicle while you are working, shopping, or even sleeping… AC chargers allows you to optimize your time! On average, a car stays parked 95%* of its time, which gives you plenty of opportunities to charge.
- On the other hand, DC chargers allow you to recover a maximum of energy fast. This method is relevant from an economic point of view when you have to charge your vehicle in a short delay. You can find these chargers in service-stations, charging hubs or even in some shops and shopping centres.
How do the characteristics of your vehicle help you make up your mind ?
To choose the power that meets your needs, you should know:
- The characteristics of the charger;
- The characteristics of your vehicle : maximum power your car can accept in AC and DC.
It turns out that a high-powered charger is not suitable for all vehicle models. Choosing a charger that delivers much more power than your vehicle can handle may be useless.
To give you an idea, the Renault Zoé has a battery capacity up to 52 kW in DC current. If you choose to connect your Renault Zoe to a charger delivering 150 kW, the maximum power accepted will not exceed 52 kW. By choosing an unsuitable charger, you block the access to other vehicles and you might pay more.
If you need more information, here are articles that might interest you : Understanding charging time and Wondering how many kilometers your electric vehicle can recover ?
As a Charge Point Operator, TotalEnergies helps and advises its customers to satisfy their needs. The company provides EV drivers with:
- Chargers from 7kW and 22kW in alternating current (AC);
- Chargers from 24kW and 50kW in direct current (DC);
- Chargers delivering up to 350kW, they are mainly available in service-stations.
Different types of plugs and connectors
Did you know ?
If you decide to charge your vehicle on a DC charger, a cable will be fixed to the charger. This is due to European regulations that requires that a cable has to be attached for security measures.
Plugs and connectors… What is the difference?
- The connector is the socket on either side of a cable, or at the end of the cable if it is attached to a charger.
- The plug is the electronic component fixed to the charger and the vehicle.
There are different types of plugs
For AC chargers
- E/F plug: This plug is available on the French market. However, the charging power stays very slow (2,2 kVA)
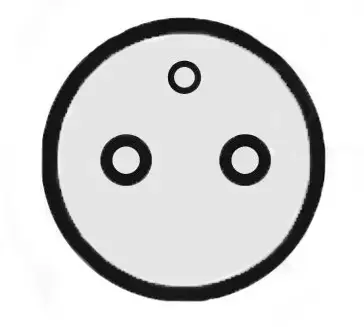
- Type 2: It is the European standard, it supports a charging power from 3,7 kW to 43 kVA
For DC chargers
There aren’t any plugs on the charger’s side, as said previously, DC chargers always have a cable fixed, for safety reasons. However, in order to receive the energy needed, your electric vehicle has a plug installed on its vehicle bodywork. This plug can vary according to your car manufacturer and the characteristics of your vehicle :
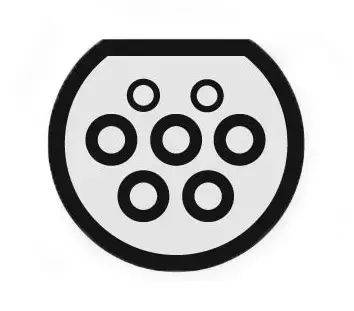
- CHAdeMO

- Combo CCS
There are different types of connectors
Indeed, there are different connectors to fit in the different plugs.
For AC chargers
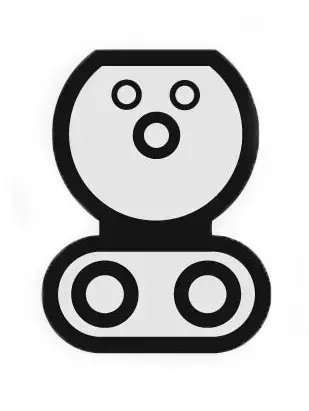
- E/F connectors
- Type 2 connectors

For DC chargers
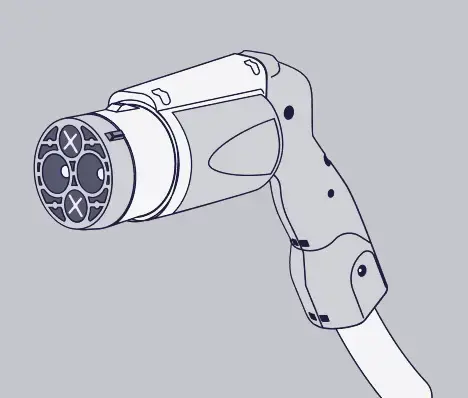
- Combo CCS : This connector is compatible with the vast majority of European and American electric vehicles
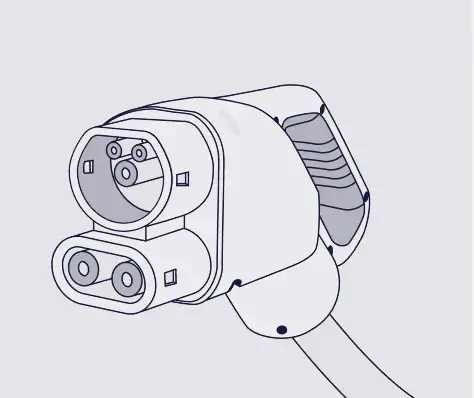
- CHAdeMO : This connector is not very common and is mainly compatible with Asian car models, such as Nissan, Mitsubishi, or Toyota. The charging power of this connector can go up to 400 kW. However, that much power can not be delivered by many chargers. Anyway, the charging power of CHAdeMO connectors allows to reduce considerably the charging time.
What you should keep in mind
You can charge your electric vehicle at home, at work or on your way at a service-station. AC chargers, delivering up to 43 kVA and allowing charging from “normal” to “accelerated”, are mainly used in the first two cases; Because EV drivers park their vehicle for a long period of time. On the other hand, DC chargers, delivering up to 350 kW, allows faster charging. They are mainly used for occasional charging sessions; Service-stations is the perfect example of where you could find DC chargers. TotalEnergies is committed to meeting the different needs of EV drivers. That’s why the Company gives the opportunity to each EV driver to find what they need by offering different chargers which deliver different levels of power.
To facilitate charging and make the use of electric vehicle a common purpose for everyone, there is a trend toward standardizing the types of plugs and connectors on a European scale around the Type 2 plug for AC chargers and the Combo CCS for DC chargers. TotalEnergies provides all types of connectors to allow each vehicle to charge on the Company’s network.
*Report Modal, ADEME 2020